Aula 3 - Estrutura de populações - crescimento populacional
Ecologia Geral 1
Felipe Melo
UFPE
2022-12-15
1 / 28
2 / 28
O que é preciso saber?
- Entender o que são parâmetros populacionais
- Entender como esses parâmetros afetam o crescimento de populações
- Calcular crescimento populacional (básico)
3 / 28
Demografia
Ciência que estuda os parâmetros populacionais envolvidos na dinẽmica de crescimento das populações
4 / 28
5 / 28
Tamanho populacional
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2021/B/K/EhNO4WRGW2A98SpyAKsw/dsc5845.jpg)
Parâmetros básicos
N = Tamanho da População
N0 = Tamanho da População Inicial
Nt = Tamanho da População no tempo T
6 / 28
7 / 28
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2021/B/K/EhNO4WRGW2A98SpyAKsw/dsc5845.jpg)
A população de jacarés cresceu de 300->500
N0 = 300
Nt = 500
Mortes?
Nascimentos?
Imigrações?
Emigrações?
8 / 28
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2021/B/K/EhNO4WRGW2A98SpyAKsw/dsc5845.jpg)
A população de jacarés cresceu de 300->500
N0 = 300
Nt = 400
Mortes (D) = 100
Nascimentos (B) = 200
Imigrações (I) = 100
Emigrações (E) = 100
9 / 28
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2021/B/K/EhNO4WRGW2A98SpyAKsw/dsc5845.jpg)
A população de jacarés cresceu de 300->500
N0 = 300
Nt = 400
Mortes (D) = 100
Nascimentos (B) = 100
Imigrações (I) = 300
Emigrações (E) = 100
10 / 28
A população de jacarés cresceu de 300->500
N0 = 300
Nt = 400
Mortes (D) = 100
Nascimentos (B) = 100
Imigrações (I) = 300
Emigrações (E) = 100
Nt = N0 +(B-D)+(I-E)
Nt - N0 = (B-D)+(I-E)
$$\Delta N = (B-D)+(I-E)$$
Este é o incrementeo populacional
11 / 28
12 / 28
Taxa de crescimento "r"
13 / 28
Taxa de crescimento "r"
N0 = Tamaho inicial = 300
13 / 28
Taxa de crescimento "r"
N0 = Tamaho inicial = 300
Nt = Tamano final = 400
13 / 28
Taxa de crescimento "r"
N0 = Tamaho inicial = 300
Nt = Tamano final = 400
Delta N = incremento = 100
13 / 28
Taxa de crescimento "r"
N0 = Tamaho inicial = 300
Nt = Tamano final = 400
Delta N = incremento = 100
$$r=\Delta N /N_0= 300/400 = 0,33$$
13 / 28
Taxa de natalidade
B/N0 = Nascidos/Ind = b
Taxa de Mortalidade
D/N0 = Nascidos/Ind = d
$$ r = \Delta N/N_0 = (b-d) $$
14 / 28
$$ \Delta N = N_0*r $$
N0 = 30 jacarés
B = 12 jacarés
b= 12/30 = 0,4
N0 = 30 jacarés
D = 6 jacarés
d= 6/30 = 0,2
15 / 28
$$ \Delta N = N_0*r $$
N0 = 30 jacarés
B = 12 jacarés
b= 12/30 = 0,4
N0 = 30 jacarés
D = 6 jacarés
d= 6/30 = 0,2
$$ \Delta N =30*(0,4-0,2) = 6$$
15 / 28
$$ \Delta N = N_0*r $$
16 / 28
$$ \Delta N = N_0*r $$
$$ N_t = N_0 + \Delta N $$
16 / 28
$$ \Delta N = N_0*r $$
$$ N_t = N_0 + \Delta N $$
$$ N_t = N_0 * (1+r) $$
16 / 28
$$ \Delta N = N_0*r $$
$$ N_t = N_0 + \Delta N $$
$$ N_t = N_0 * (1+r) $$
$$ N_t = N_0 * \lambda^t $$
$$ \lambda = crescimento$$
16 / 28
Crescimento geométrico - Populações semélparas
tempo<-seq(1:10) populacao<-(2^seq(1,10,by=1))data<-data.frame(tempo,populacao)library(ggplot2)ggplot(data=data, aes(tempo,populacao))+geom_line(group=1)+geom_point()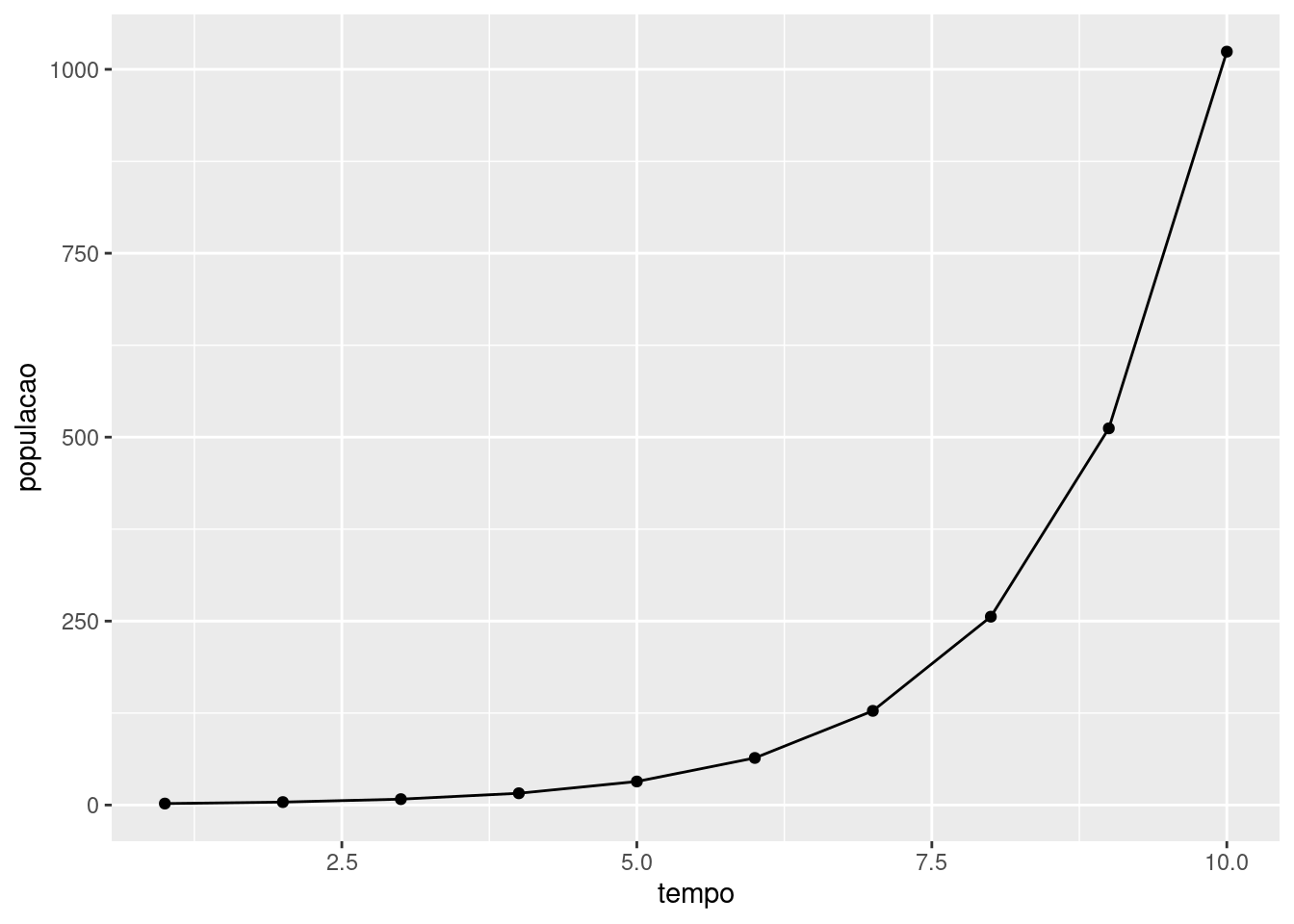
17 / 28
Crescimento geométrico
tempo<-seq(1:10) populacao2<-(3^seq(1,10,by=1))data2<-data.frame(tempo,populacao2)library(ggplot2)ggplot(data=data2, aes(tempo,populacao2))+geom_line(group=1)+geom_point()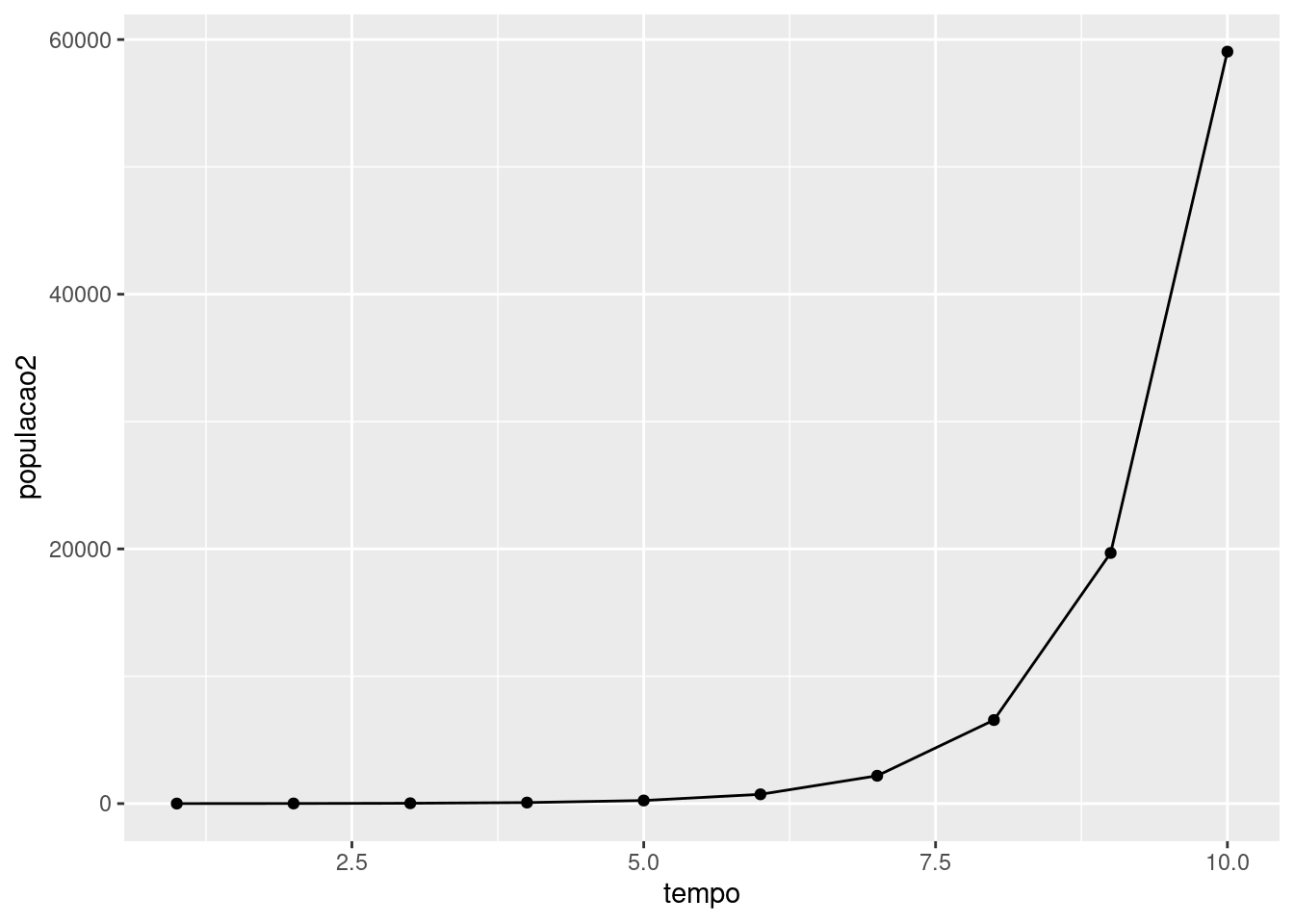
18 / 28
Crescimento geométrico negativo
tempo<-seq(1:10) populacao3<-(0.7^seq(1,10,by=1))*100data3<-data.frame(tempo,populacao3)library(ggplot2)ggplot(data=data3, aes(tempo,populacao3))+geom_line(group=1)+geom_point()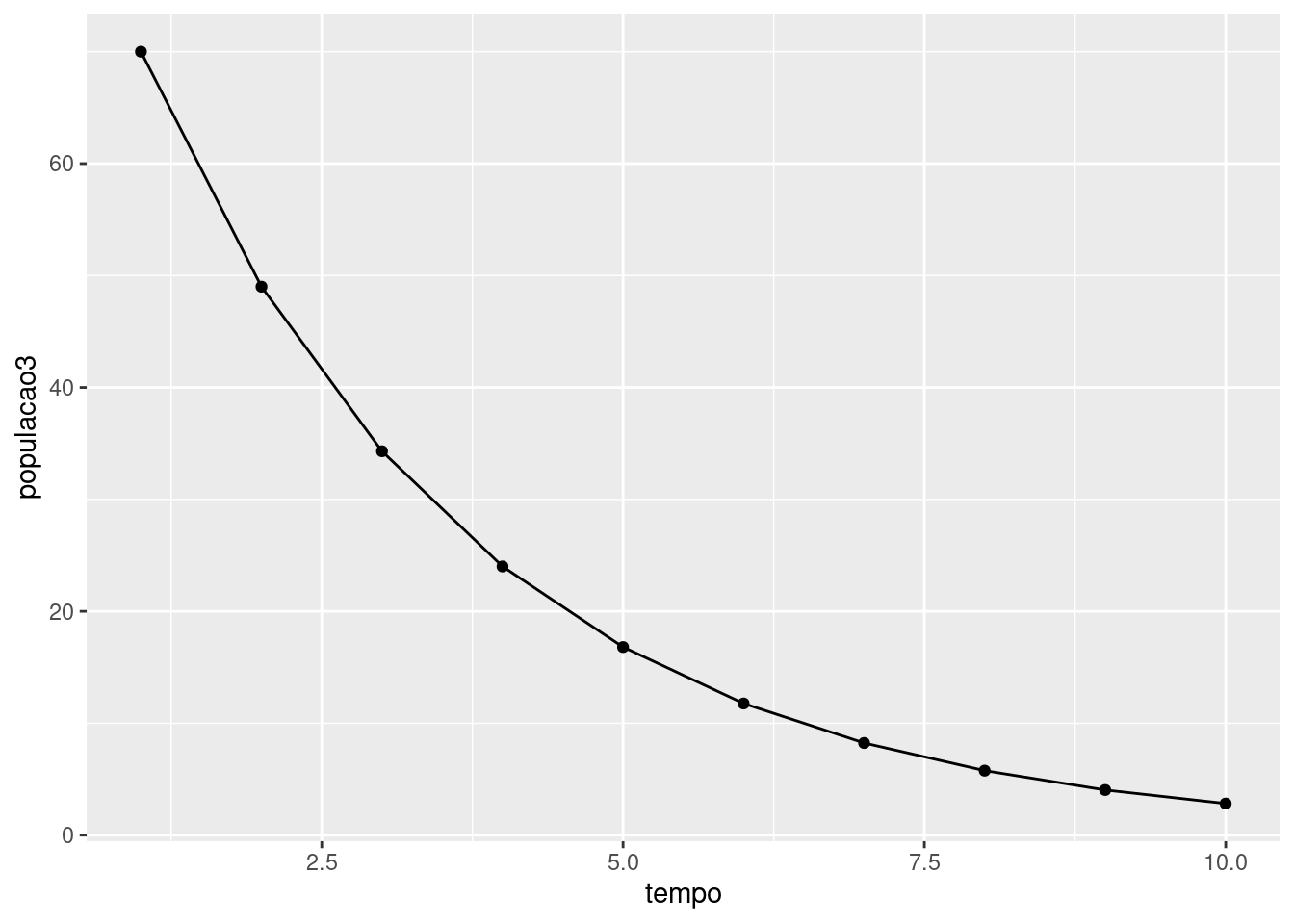
19 / 28
Crescimento exponencial - Populações iteróparas
Crescimento geométrico
$$N_t = N_0 * \lambda^t$$
Nt = filhos
N0 = pais
$$\lambda^t = filhos/pais$$
Crescimento exponencial
$$N_t = N_0 * e^{rt}$$
Nt = filhos + pais
N0 = pais
$$ e^{rt} = b + pais - mortos$$
20 / 28
Crescimento exponencial
tempo<-seq(1:100)f<-exp(0.03*tempo)populacao4<-100*seq(100, along.with=tempo)*fdata4<-data.frame(tempo,populacao4)library(ggplot2)ggplot(data=data4, aes(tempo,populacao4))+geom_line(group=1)+geom_point()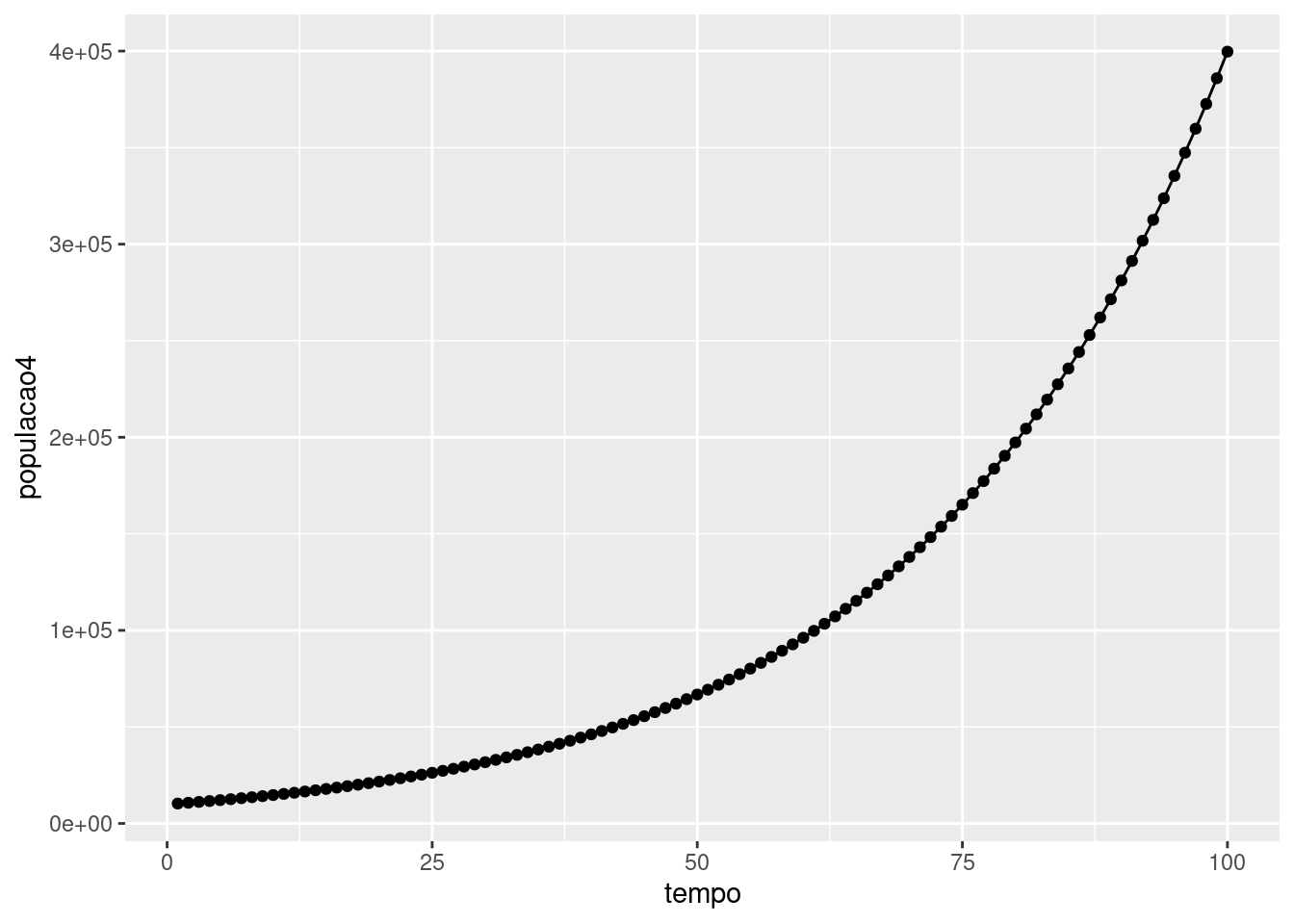
21 / 28
Crescimento exponencial
tempo<-seq(1:100) f<-exp(0.1*tempo)populacao4<-seq(10, along.with=tempo)*fdata4<-data.frame(tempo,populacao4)library(ggplot2)ggplot(data=data4, aes(tempo,populacao4))+geom_line(group=1)+geom_point()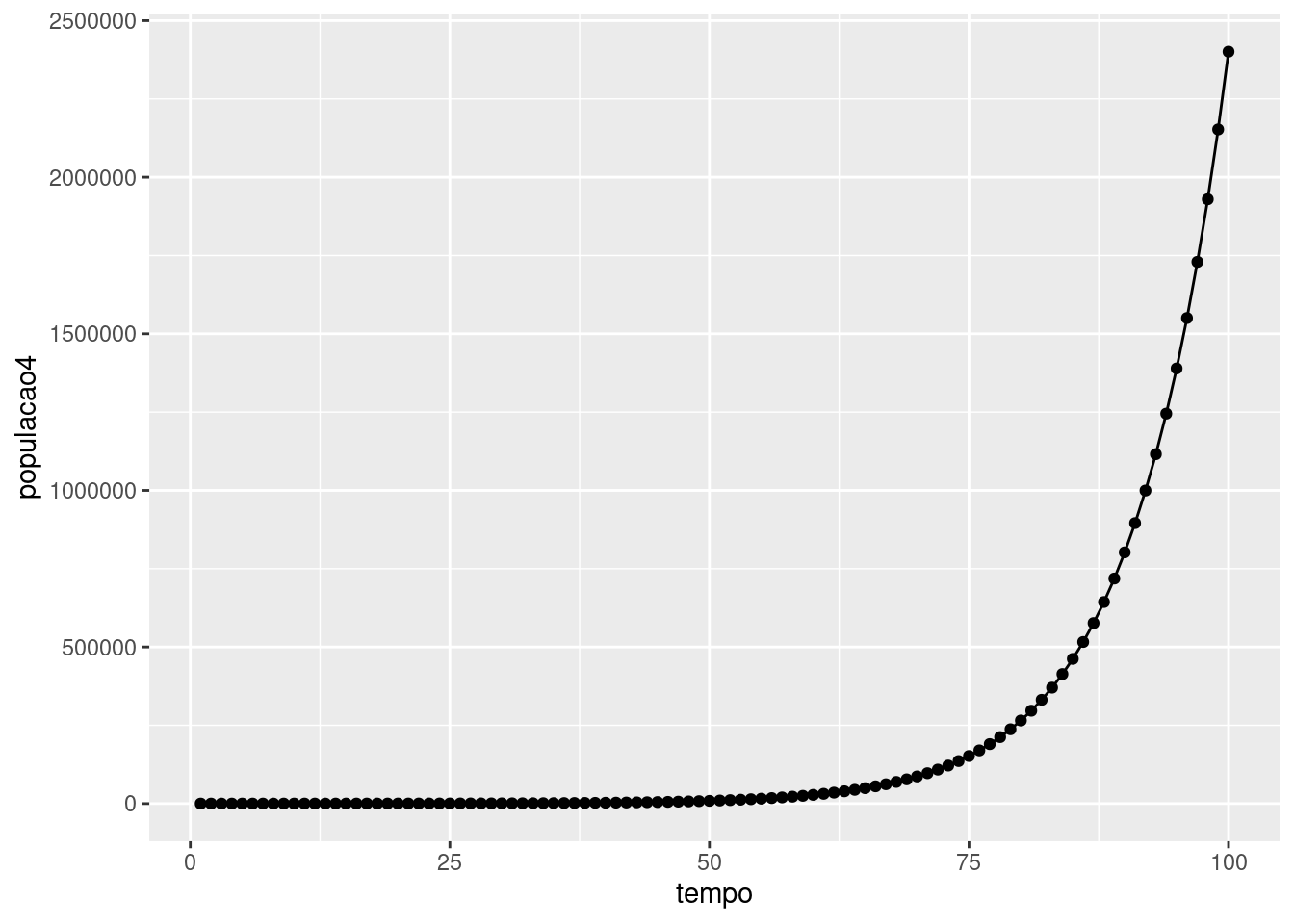
22 / 28
Crescimento exponencial
tempo<-seq(1:100) f<-exp(-0.1*tempo)populacao4<-seq(1000, along.with=tempo)*fdata4<-data.frame(tempo,populacao4)library(ggplot2)ggplot(data=data4, aes(tempo,populacao4))+geom_line(group=1)+geom_point()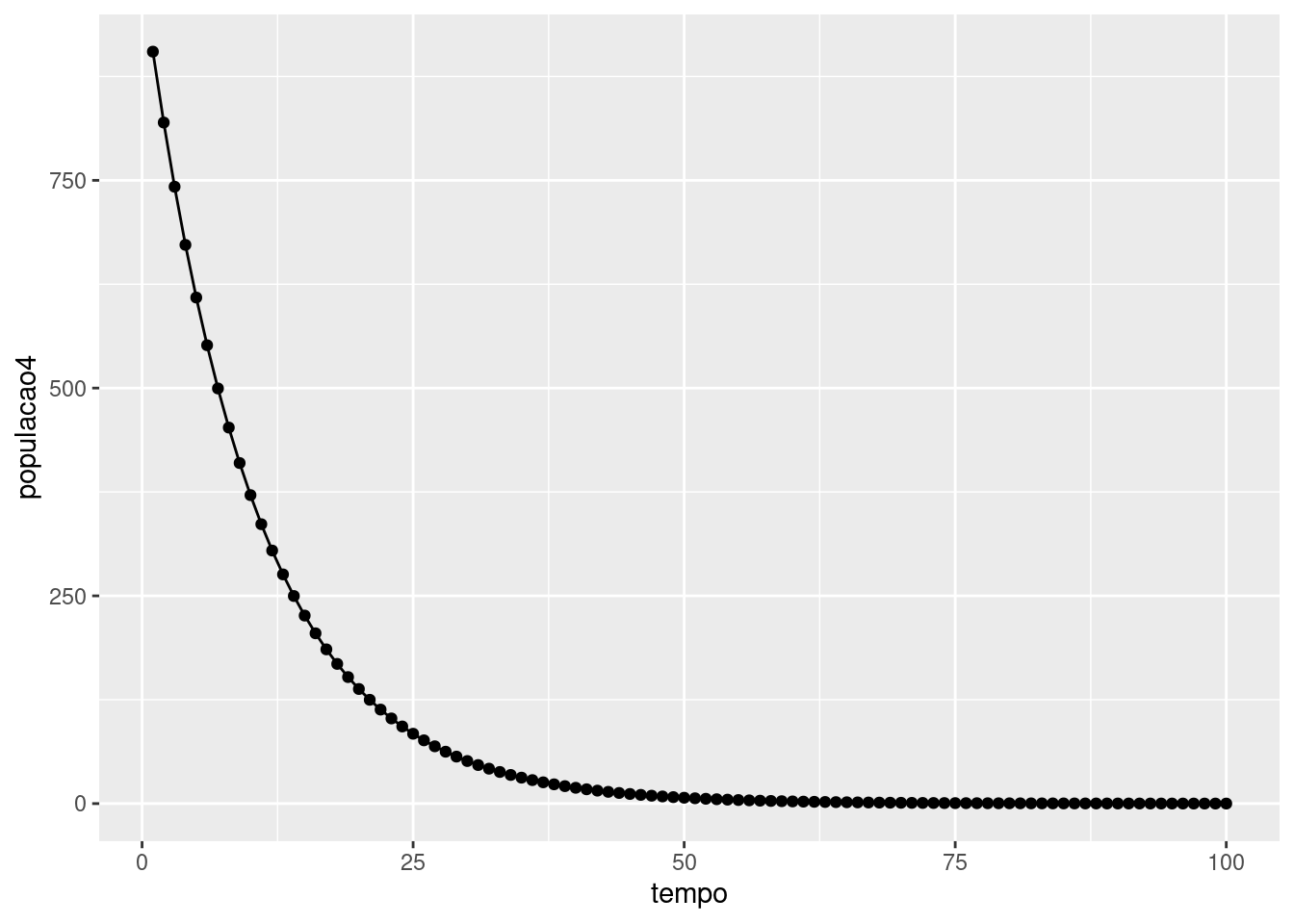
23 / 28
fatores que influenciam as taxas intrínsecas (r)
- Nicho ecológico
- Adequação dos indivíduos
- História de vida (r ou K estrategistas)
- Capacidade de carga dos ecossistemas (K)
24 / 28
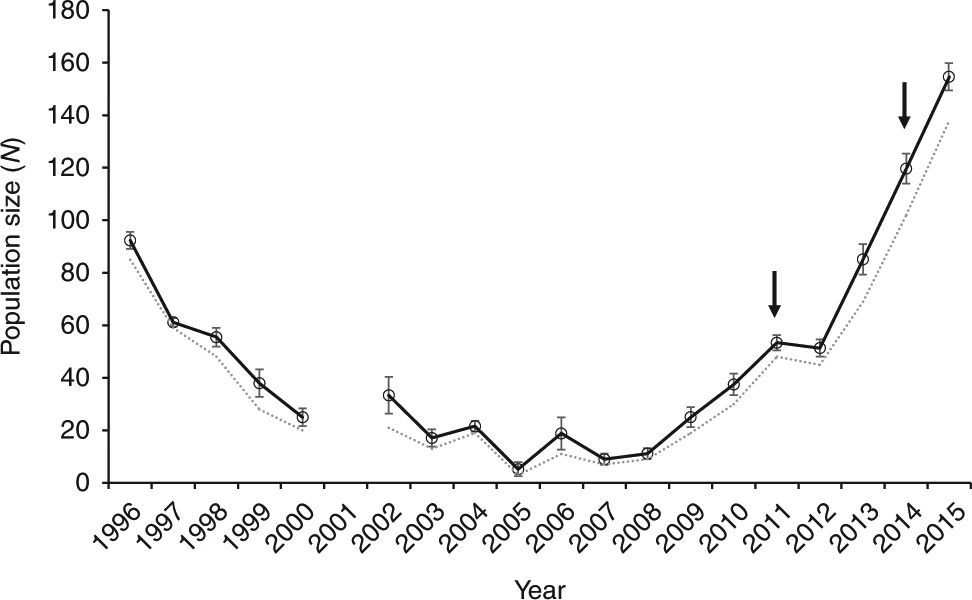
No mundo real...
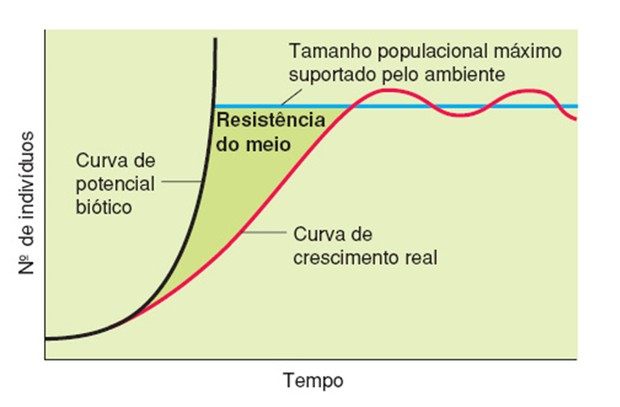
25 / 28
Espécies invasoras
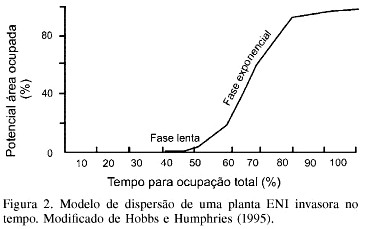 fonte: https://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0378-18442007000900004
fonte: https://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0378-18442007000900004
26 / 28

27 / 28
Por hoje é só.
28 / 28